If you made contributions to or distributions from your HSA in 2017, you will need to file the federal tax form 8889. This form is specific to HSA’s and records all activity with your HSA for the year. It flows to Form 1040 to adjust your income: your contributions reduce your taxable income, whereas any penalties adds back to income, increasing tax.
Form 8889 is not as straightforward as it could be, so I created a service called EasyForm8889.com that completes your form for you. I have also created the following video to walk through how to file Form 8889. Little has changed since the 2016 form used in this video. Check it out, otherwise, the transcription of the information is below.
Watch on Youtube: How to File HSA Tax Form 8889
In the following article we will cover:
- Changes to 2017 Form 8889
- 2017 HSA Contribution Limits
- 2017 HDHP Definitions
- 2017 Form 8889 instructions and example
Changes to 2017 Form 8889 tax form
The 2017 HSA tax form presents little difference to prior year tax forms. Throughout the form you will see the tax year incremented to 2017, so make sure you are working on the correct version. This can be confirmed in the upper right of the form. Contribution limits have increased in 2017, so these amounts are reflected throughout the form (specifically Line 3).
There were also some changes to HDHP definitions in 2017 so read on if those apply to you.
Changes to 2017 Form 8889 instructions
The 2017 Form 8889 instructions have been released by the IRS and can be found here. They are substantially the same as prior years save for year and contribution limit updates.
2017 HSA Contribution Limits
For self-only coverage, the maximum contribution limit increased by $50 to $3,400 in 2017. There were no changes to the family coverage amount which is $6,750, as well as the 55+ catch up contribution amount of $1,000. The IRS defines the maximum amounts that may be contributed to a Health Savings Account each year. Per IRS Publication 969:
The amount you or any other person can contribute to your HSA depends on the type of HDHP coverage you have, your age, the date you became an eligible individual, and the date you cease to be an eligible individual…for 2017, if you have self-only HDHP coverage, you can contribute up to $3,400. If you have family HDHP coverage you can contribute up to $6,750.
Here are HSA contribution limits for prior years:
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Self-Only HSA Contribution Limit | $3,300 | $3,350 | $3,350 | $3,400 |
| Family HSA Contribution Limit | $6,550 | $6,650 | $6,750 | $6,750 |
| 55+ Additional Contribution Limit | +$1,000 | +$1,000 | +$1,000 | +$1,000 |
The maximum contribution amount for your HSA in 2017 is $3,400 for self-only coverage and $6,750 for family. Note that this does not include the additional 55+ catch up contribution of $1,000 allowed to properly aged HSA holders. Thus, if you are over 55 on or before the end of 2017, you can contribute $4,400 for self-only coverage or $7,750 for family coverage.
2017 HDHP Definitions
To qualify as an HDHP, your health plan cannot exceed an out-of-pocket maximum limit established by the IRS. There were no changes to these amounts from 2016 to 2017. For self-only plans, the minimum deductible remains $1,300 and the out of pocket maximum is $6,550. For Family plans, the minimum deductible is $2,600 while the out of pocket maximum is $13,100. Plans with a deductible below that specified are not HSA eligible, nor are plans with an out-of-pocket max greater than those listed. The HDHP definitions for recent years are summarized below:
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Self-Only Min Deductible | $1,250 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 |
| Self-Only OOP Max | $6,350 | $6,450 | $6,550 | $6,550 |
| Family Min Deductible | $2,500 | $2,600 | $2,600 | $2,600 |
| Family OOP max | $12,700 | $12,900 | $13,100 | $13,100 |
2017 HSA Form 8889 example
Let’s walk through an example of the 2017 Form 8889 to show how it works.
Let’s assume I am a married 40 year old who had family HSA eligible coverage from January – June of 2017 (6 months). On July 1st, I changed to a non-HSA eligible plan. My spouse does not have their own Health Savings Account. I contributed $1,800 to my HSA and my employer contributed $800. I distributed $800 from the HSA during the year, all of which I spent on qualified medical expenses.
Part I – Contributions and Deduction
Form 8889 starts off pretty simply on Line 1 by asking the type of insurance you had (mostly) during the year. For this example, it is family. Line 2 then goes on to ask how much you contributed to your HSA during the year. In our case this was $1,800, which does not include employer contributions. Line 3 can be quite complicated, but in essence you need to list your contribution limit for the year. If you had self-only or family coverage all year, the amounts are provided for you. Otherwise, you need to prorate your coverage by month. In this case, we had family coverage for 6 months, so our contribution limit is $3,375 for 2017. Line 4 asks about Archer MSA’s (does not apply here) and Line 5 is a simple subtraction.
[Note: all 2017 tax forms were generated in minutes using EasyForm8889.com]
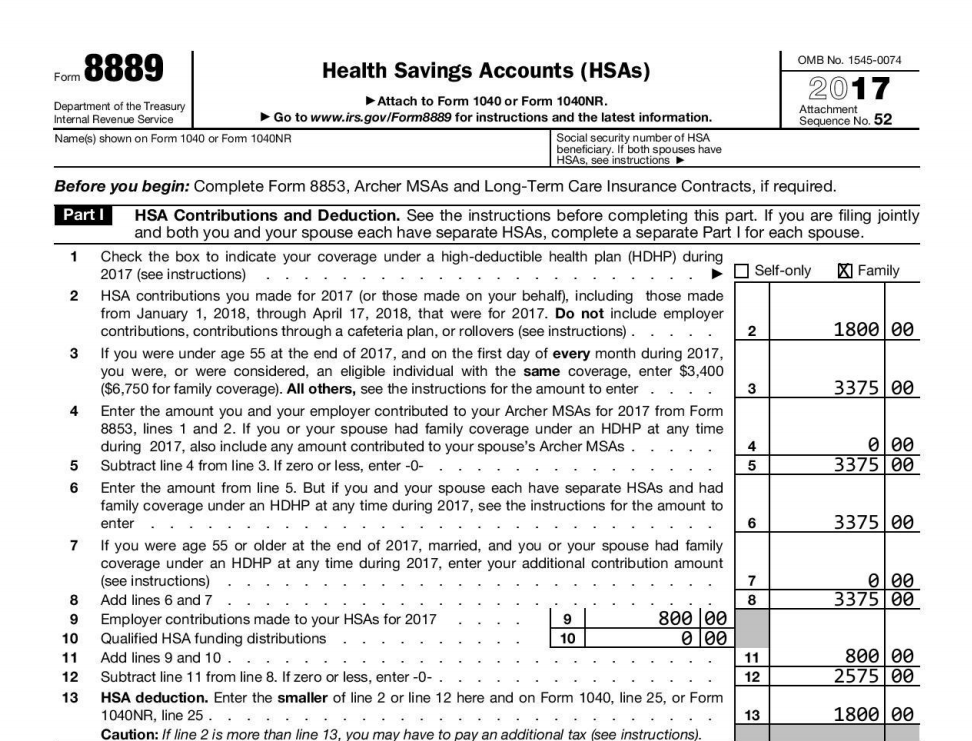
We continue with Line 6, which for self-only filers equals Line 5. For family coverage where both spouses have their own Health Savings Account, each of you needs to file your own Form 8889. Then on Line 6, you allocate the share of the contribution limit that belongs to that HSA. In this case, only the insured has an HSA, so this line equals Line 5. For some situations, Line 7 adds the $1,000 catch up contribution, but our example assumes the HSA holder is 40 years old so this does not apply. Line 8 is simple subtraction, and the $800 employer contribution comes into play on Line 9. If you contributed to your HSA from an IRA you would indicate that on Line 10, and Line 11 is simple addition. Line 12 is subtraction, and Line 13 does a comparison to calculate what your 2017 HSA deduction is, which makes its way to Form 1040. In our case, it is the $1,800 we contributed to the HSA.
Part II – Distributions
The second part of the 2017 Form 8889 deals with distributions, or amounts that came out of your HSA. We assume that we distributed $800 from the HSA, so that amount is shown on Line 14a. Line 14b lists rollover amounts and excess contributions that were removed, and Line 14c subtracts them out. The filer tracked his qualified medical expenses and receipts using TrackHSA.com this year, so he can easily prove all $800 in distributions were used for medical expenses. He places that amount in Line 15. A subtraction occurs on Line 16 to determine any amounts not spent on qualified medical expenses; luckily that is $0 for us. If you had an amount on Line 16, Line 17a gives you the chance to exclude this from taxation based on a few exceptions. Otherwise, that Line 16 amount is taxed 20% on Line 17b, which gets recorded on Form 1040.

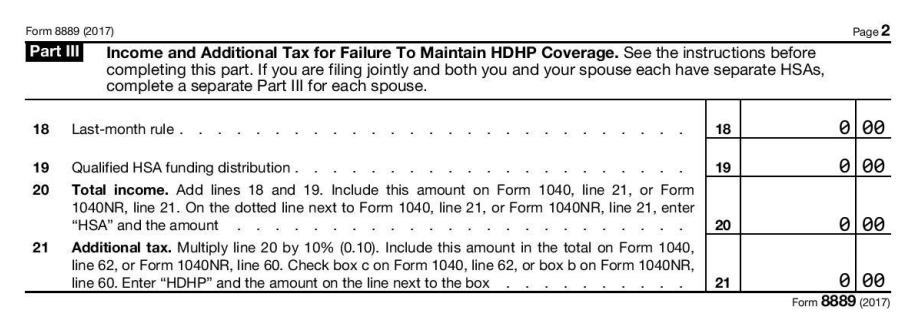
Part III – Penalties and Taxes
For most people, Part III will look a lot below: all zeroes. This is good, but it is possible that you have accrued some taxes and penalties. If in the prior tax year, you 1) used the Last Month Rule and proceeded to 2) fail its Testing Period, a difficult calculation awaits you on Line 18. You are going to have to go back, figure out how much you contributed in the prior year, redetermine what you could have contributed without the Last Month Rule, and place the difference here. On a similar note, if you made a qualified funding distribution from your IRA but failed its Testing Period in 2017, you will have to enter the amount that failed in Line 19. Once that is done, Line 20 adds Line 18 and Line 19 and adds it back to income (where it is taxed) on Form 1040. Finally, for good measure, Line 21 assesses a 10% penalty against the amount on Line 20, which also makes its way to Form 1040.
Note: if you need help with your 2017 Form 8889, or just want it done right now, please consider using my service EasyForm8889.com. It asks simple questions in a straightforward way and will generate your completed HSA tax forms in 10 minutes. It is fast and painless, no matter how complicated your HSA situation.







